How to spot fake news
False reports spread extremely quickly, especially on social media and messenger services. There are also countless videos and images circulating about the war in Ukraine, some of which turn out to be false or are unverified. It is all the more important not to spread such news unchecked and thoughtlessly.
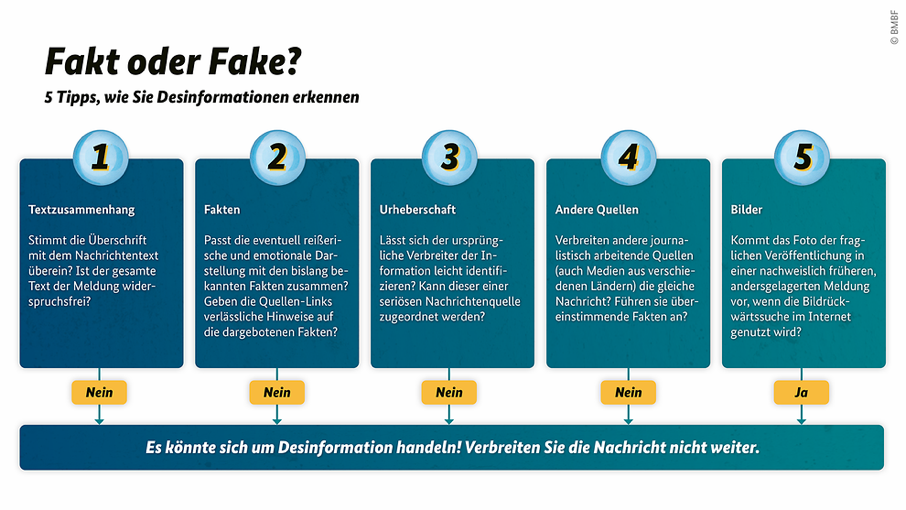
What is fake news?
Fake news is news that is partially or completely fabricated. Translated, the English term means “fake news”. Fake news is often related to current events and often looks like journalistic articles. People should think that the information is real.
Pictures and videos can also be processed to a great extent with today’s technology. That means you can delete things on pictures or videos. However, things that cannot be seen in the original can also be inserted. These edits are difficult to see.
There has always been false news. But thanks to the Internet, they spread much faster than they used to – especially when shared on social media.
Use fact checks
The linked sources can provide indications of how reliable the facts of the message are. To check whether information is true, you can enter suspicious keywords from the message text into a search engine along with the word fact check.
For example, public service media and other independent organizations review and correct individual false reports. Among other things, the independent research center Correctiv documents and analyzes current and internationally circulating disinformation and false reports about the war in Ukraine. The European External Action Service (EEAS) lists current cases of disinformation from Russia on its website EUvsDisinfo.eu – and refutes false claims.
Check the sender of the message
Always check who posted the video, picture or message. Is he or she the originator of the material or has it been shared multiple times? The indication of a real name can be an indication of the authenticity of an account. For websites, look at the imprint. The information should include a person responsible for the website content and a full address, not just an anonymous email address, for example.
Compare sources
It always helps to compare questionable messages with other sources. The fact-check departments of many reputable media regularly and regularly check image and video material. You can also find out more on the official websites of the public institutions.
Check images
Whether a photo has been manipulated or is an original can be checked with the help of the image reverse search: The image file or the URL is uploaded to a search engine page, where available, information about the place and date of publication on the Internet. For example, it is also possible to find out whether an image is up-to-date at all or perhaps comes from earlier publications, possibly in a completely different context.
Identify, understand and fight fake news
Fueling uncertainty, manipulating opinions, shaking trust: fake news is a threat to our democracy and society. The BMBF is therefore funding researchers who want to better understand and combat such targeted disinformation.
The Federal Ministry of Research sees fake news as an increasing threat to democracy and social cohesion. That is why the BMBF is now funding ten new projects in which scientists are researching fake news and other forms of disinformation in order to develop countermeasures.
These are the funded projects:
In the project “DeFaktS – Recognize and disclose factors and stylistic devices of disinformation campaigns”, researchers analyze messages from social media and messenger groups. They want to use the data to train artificial intelligence. She should learn to recognize the factors and stylistic devices that are characteristic of disinformation. The aim of the project is an app that warns its users when suspicious stylistic devices appear in messages.
In the project “DYNAMO – Understanding, recognizing and combating highly dynamic forms of dissemination of disinformation”, researchers are investigating how disinformation spreads in messenger services and how it “spills over” into other social media. They also analyze the extent to which there are recurring patterns from which control strategies can be derived. Research is also to be carried out into the patterns behind disinformation campaigns and the influence that emotional content has on dissemination. The aim is to develop instruments that counteract the spread of disinformation.
Exploring narratives of disinformation in public service and alternative news videos”, researchers examine the narratives of disinformation in public service news programs and alternative information videos. In doing so, they use discourse and linguistic analyzes as well as investigative methods from the digital humanities Patterns are recognized using machine learning The aim is a digital tool that can systematically reveal mechanisms and strategies of narratives of disinformation.
Real-time detection of disinformation campaigns in online media”, researchers are developing a software-based analysis tool that is intended to help experts to better assess disinformation campaigns. The researchers combine machine analysis with human expertise to identify disinformation campaigns. The analysis tool should enable large Evaluating amounts of data from online media and social networks in real time and recording temporal patterns.On this basis, experts can comprehensively assess disinformation campaigns and their effects.
Efficient fact checks through artificial intelligence and crowdsourcing”, researchers are developing an assistance system for the detection of disinformation, which is intended to automatically sift through large amounts of data: suspicious text and image material is pre-sorted, linked to similar material and the distribution paths of the material are traced. The assistance system should Finally, support previously trained staff in assessing the trustworthiness of information material.
The role of celebrities in disinformation campaigns in the eyes of science” researchers are investigating the role celebrities play in political communication and in spreading disinformation on social media. Since celebrities are usually represented on multiple digital platforms, they can serve as markers for the Disinformation spread across platforms A scientific analysis of the disinformation spread paths they emanate should be used to explore the underlying spread patterns.
Training approach to conveying measures to prevent digital disinformation campaigns”, researchers want to enable offices, authorities and organizations to counteract intentional manipulation of opinion. To this end, the researchers are developing a training tool that simulates the emergence and targeted dissemination of disinformation and the effect of the The simulations are based on realistic training scenarios (e.g. Covid-19 pandemic).
“Recognizing and combating disinformation on health topics with artificial intelligence”, researchers want to create a data set that includes information from public news portals, social media as well as technical and expert knowledge. They use data mining and artificial methods to extract and structure the data Intelligence: With the help of the data set, citizens looking for information should be able to identify forgeries and disinformation more quickly.
Resources:
- https://www.bundesregierung.de/breg-de/themen/umgang-mit-desinformation/falschmeldungen-erkennen-1750146
- https://www.pasch-net.de/de/lernmaterial/wissen-umwelt/fakt-oder-fake.html
- https://www.bundesregierung.de/breg-de/themen/umgang-mit-desinformation
- https://www.bmbf.de/bmbf/shareddocs/kurzmeldungen/de/2022/02/fake-news-bekaempfen.html
- https://www.bmbf.de/bmbf/de/home/home_node.html